The efficacy and safety of CABLIVI were established in one of the largest acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP/iTTP) clinical studies1,2
HERCULES was a pivotal, phase 3, double-blind, randomized controlled trial of 145 patients with aTTP/iTTP assessing the efficacy and safety of CABLIVI in combination with PEX and immunosuppressive therapy.
Who should not start CABLIVI?
- CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients
- Withhold CABLIVI treatment 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures, or other invasive interventions
HERCULES study design
A pivotal, phase 3, double-blind, randomized controlled trial of 145 patients with aTTP/iTTP; patients were given PEX and immunosuppressive therapy in the form of corticosteroid treatment. Other immunosuppressive treatments, such as rituximab, were permitted but not required.*
Patients were then randomized to receive CABLIVI (72) or placebo (73) for the duration of daily PEX and 30 days thereafter. Patients could receive extended treatment for up to 28 days if signs of underlying disease persisted, such as suppressed ADAMTS13 activity levels.1,2
Key efficacy endpoints1,2

Primary endpoint: Time to platelet count normalization§

Secondary endpoint: Composite of aTTP/iTTP-related events during study-drug period, including: aTTP/iTTP-related death, recurrence,‡ and ≥1 major TE event

Secondary endpoint: Recurrence during overall study period‡
*2 patients in each group did not receive any immunosuppressive therapy.
†Daily PEX was variable based on platelet count normalization at ≥150,000/μL and physician discretion.2
‡Thrombocytopenia after initial recovery of platelet count (platelet count ≥150,000/μL) that required reinitiation of daily PEX was considered a recurrence. Recurrences were termed exacerbations if they occurred within 30 days of the last PEX and relapses if they occurred more than 30 days after the last PEX.2
§Platelet count normalization was defined as platelet count ≥150,000/μL with discontinuation of daily PEX 5 days thereafter.2
Select Demographic and Baseline Characteristics in the Study Population2
| CABLIVI | Placebo | Total | |
| Characteristic | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) |
| IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE THERAPY—NO. (%) | |||
| Glucocorticoids | 69 (96) | 71 (97) | 140 (97) |
| Rituximab | 28 (39) | 35 (48) | 63 (43) |
| Other|| | 12 (16) | 3 (3) | 15 (10) |
| PRESENTING EPISODE OF TTP—NO. (%)¶ | |||
| Initial | 48 (67) | 34 (47) | 82 (57) |
| Recurrent | 24 (33) | 39 (53) | 63 (43) |
| ADAMTS13 ACTIVITY—NO. (%)# | |||
| <10% | 58 (81) | 65 (89) | 123 (85) |
| ≥10% | 13 (18) | 7 (10) | 20 (14) |
Key Inclusion Criteria: ≥18 years of age; clinical diagnosis of aTTP/iTTP; required initiation of daily PEX and received PEX prior to randomization.
Key Exclusion Criteria: Platelet count ≥100 × 109/L or >30 × 109/L if serum creatinine level >200 µmol/L; known other causes of thrombocytopenia, such as congenital TTP, pregnancy, or breastfeeding; clinically significant active bleeding or high risk of bleeding; known chronic treatment with anticoagulants; malignant arterial hypertension; life expectancy <6 months.
‖Other immunosuppressive therapies include, for CABLIVI and placebo respectively: mycophenolate mofetil (6, 0), hydroxychloroquine (2, 1), bortezomib (2, 0), cyclophosphamide (1, 1), cyclosporin (1, 1).
¶The difference between the trial groups in the percentage of patients who presented with an initial episode as compared with a recurrent episode was significant (P<0.05).2
#The normal range of ADAMTS13 activity used in the trial was 50% to 130%. As a result of the requirement for previous plasma exchange, baseline ADAMTS13 activity was higher than that measured locally at the time of admission in some cases. When available, ADAMTS13 activity levels that were locally measured at the time of admission were obtained, and the lower value of the baseline and admission values is represented.2
Efficacy
In combination with PEX and immunosuppressive therapy,
CABLIVI helped to normalize platelet counts faster, reduced potentially serious aTTP/iTTP-related events, and had significantly fewer recurrences requiring reinitiation of PEX1,2
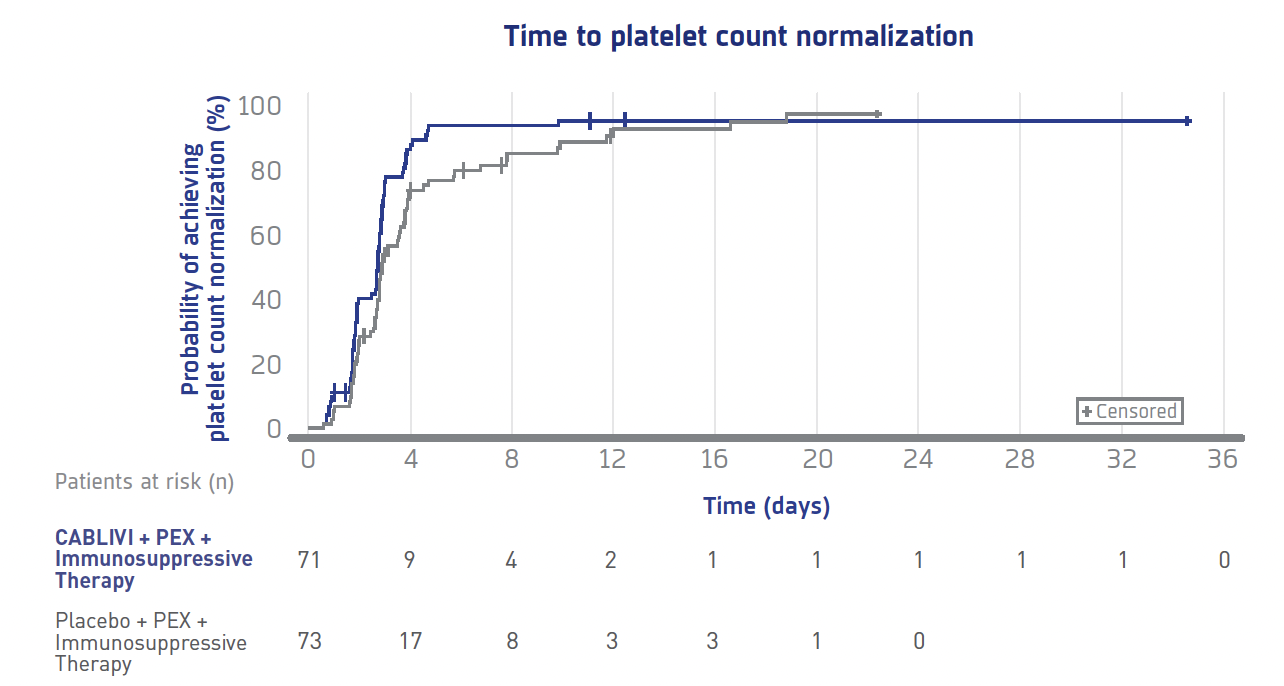
Patients achieved normal platelet count significantly faster with CABLIVI§
The CABLIVI group (72)** reached platelet count normalization§ significantly faster than the PEX and immunosuppressive therapy group (73).

SIGNIFICANTLY FASTER
time to platelet normalization§ with CABLIVI
Time to platelet count response
CABLIVI significantly reduced potentially fatal and serious aTTP/iTTP-related events
Compared with PEX and immunosuppressive therapy alone (73), the CABLIVI group (72) demonstrated a significant reduction in a composite endpoint of aTTP/iTTP-related events (36 [49.3%] vs 9 [12.7%], respectively):
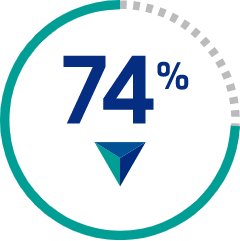
74% REDUCTION IN aTTP/iTTP-RELATED EVENTS
(P<0.0001)
Total composite endpoint of aTTP/iTTP-related events during the study-drug period
| CABLIVI + PEX + Immunosuppressive Therapy |
Placebo + PEX + Immunosuppressive Therapy |
|
| N=72, n (%)** | N=73, n (%) | |
| aTTP/iTTP-related death | 0 | 3 (4.1%) |
| Recurrence during treatment‡ | 3 (4.2%) | 28 (38.4%) |
| ≥1 major thromboembolic event | 6 (8.5%) | 6 (8.2%) |
| Total | 9 (12.7%) | 36 (49.3%) |
Four aTTP/iTTP-related deaths occurred during the trial, including 1 non–treatment-related death in the CABLIVI group during the treatment-free follow-up period and 3 deaths in the placebo group during the treatment period.2
CABLIVI resulted in significantly fewer recurrences requiring reinitiation of PEX‡
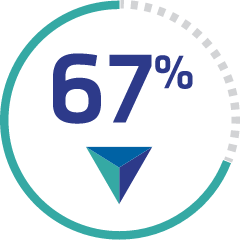
67% REDUCTION IN RECURRENCE
during treatment and through 28 days post-treatment vs PEX and immunosuppressive therapy alone 9 (13%) vs 28 (38%), respectively; P<0.001
Incidence of recurrences during treatment and throughout the 28-day follow-up post-treatment
6 patients required reinitiation of PEX after treatment with CABLIVI was stopped
- These patients had ADAMTS13 activity levels <10%, indicating the underlying disease was still active when treatment was stopped
Suppressed ADAMTS13 activity may signify the need to extend CABLIVI treatment
‡Thrombocytopenia after initial recovery of platelet count (platelet count ≥150,000/μL) that required reinitiation of daily PEX was considered a recurrence. Recurrences were termed exacerbations if they occurred within 30 days of the last PEX and relapses if they occurred more than 30 days after the last PEX.2
§Platelet count normalization was defined as platelet count ≥150,000/μL with discontinuation of daily PEX 5 days thereafter.2
**71 patients received at least 1 dose of study drug.
Healthcare resource utilization
Days in the ICU, in the hospital, and receiving PEX during treatment2
In the phase 3 trial of CABLIVI in combination with PEX and immunosuppressive therapy for patients with aTTP/iTTP, data for patient time spent in the ICU, in the hospital, and receiving PEX were collected prospectively. Descriptive statistics were run, but these data were not tested for significance. The clinical significance of these data is unknown.
Healthcare resource utilization
Average volume of plasma exchanged
21.3 L
CABLIVI + PEX + Immunosuppressive Therapy
35.9 L
Placebo + PEX + Immunosuppressive therapy alone
In HERCULES, the median duration of treatment
with CABLIVI was 35 days
Safety
The safety of CABLIVI was established in more than 100 patients across 2 studies1††
Overall bleeding events
58%
CABLIVI group
vs
43%
PEX + immunosuppressive therapy alone
Severe bleeding was reported in 1% of patients for each of the following events:

Epistaxis

Gingival bleeding

Upper GI hemorrhage

Metrorrhagia
Most frequent adverse reactions in phase 2 and phase 3 clinical studies
|
CABLIVI + PEX + |
PEX + |
||
| GI disorders | Gingival bleeding |
17 (16) |
3 (3) |
| Rectal hemorrhage | 4 (4) | 0 (0) | |
| Abdominal wall hematoma | 3 (3) | 1 (1) | |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Fatigue | 16 (15) | 10 (9) |
| Pyrexia | 14 (13) | 12 (11) | |
| Injection site hemorrhage | 6 (6) | 1 (1) | |
| Catheter site hemorrhage | 6 (6) | 5 (5) | |
| Injection site pruritus | 3 (3) | 0 (0) | |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders |
Back pain | 7 (7) | 4 (4) |
| Myalgia | 6 (6) | 2 (2) | |
| Nervous system disorders | Headache | 22 (21) | 15 (14) |
| Paresthesia | 13 (12) | 11 (10) | |
| Renal and urinary disorders | Urinary tract infection | 6 (6) | 4 (4) |
| Hematuria | 4 (4) | 3 (3) | |
| Reproductive system and breast disorders | Vaginal hemorrhage | 5 (5) | 2 (2) |
| Menorrhagia | 4 (4) | 1 (1) | |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | Epistaxis | 31 (29) | 6 (6) |
| Dyspnea | 10 (9) | 5 (5) | |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
Urticaria‡‡ |
15 (14) | 7 (6) |
††Adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with CABLIVI and that occurred more frequently than placebo during the blinded periods of the phase 2 and phase 3 studies.
‡‡Urticaria was seen during PEX.
Enroll patients in CABLIVI Patient Solutions to give eligible patients access to educational resources and financial assistance
Learn key information related to the procurement of CABLIVI
The CABLIVI dosing regimen starts in the hospital and continues at home
Enroll your patients in CABLIVI Patient Solutions
ADAMTS13=a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin type 1 motif, 13; GI=gastrointestinal; ICU=intensive care unit; PEX=plasma exchange; TE=thromboembolic; TTP=thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. CABLIVI. Prescribing information. Genzyme Corporation. 2. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346 and suppl/protocol. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. CABLIVI. Prescribing information. Genzyme Corporation. 2. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346 and suppl/protocol. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. CABLIVI. Prescribing information. Genzyme Corporation. 2. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346 and suppl/protocol. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. CABLIVI. Prescribing information. Genzyme Corporation. 2. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346 and suppl/protocol. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. CABLIVI. Prescribing information. Genzyme Corporation. 2. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346 and suppl/protocol. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. CABLIVI. Prescribing information. Genzyme Corporation. 2. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346 and suppl/protocol. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311

