What is aTTP/iTTP?
Acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP/iTTP) is a rare, life-threatening, thrombotic microangiopathy manifested as microvascular thrombi and consequent thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, and organ ischemia.2 Thrombotic microangiopathies (TMAs), such as aTTP/iTTP, can be hard to differentiate.6,7
Learn more about the different TMAs and how to distinguish one from another.
Types of TTP8-10
Acquired/immune-mediated TTP
- The most common form of TTP; accounts for 95% of TTP cases
- Caused by autoantibody inhibition of ADAMTS13 activity
Hereditary TTP
(also known as congenital TTP, inherited TTP, familial TTP, or Upshaw-Schulman syndrome)
- Rare form of TTP
- Caused by mutations in the ADAMTS13 gene
≈95% of TTP cases are aTTP/iTTP8
Each aTTP/iTTP episode can be unpredictable with microthrombi-driven risks5,11,12
The pathophysiology of aTTP/iTTP poses a triple threat; PEX and immunosuppressive therapy directly address only 2 of the 3 aspects of the disease9,13-18

Patient risk may remain in aTTP/iTTP despite treatment with PEX and immunosuppressive therapy4
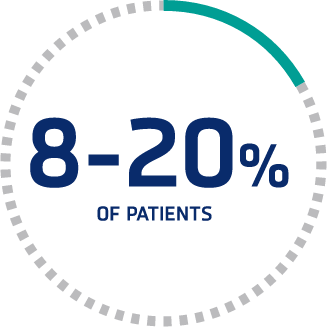
Mortality remains high
8% to 20% of patients die despite receiving PEX and immunosuppressive therapy, according to a range of studies.1,2,4*
*Literature review of studies with more than 100 patients with TTP.
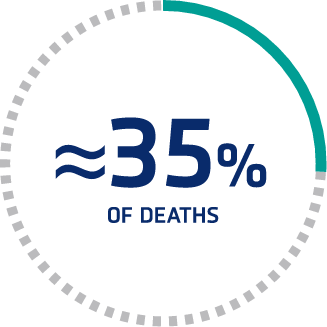
Thromboembolic events caused by ischemia are common
Nearly 35% of in-hospital TTP deaths (613) were related to ischemia, including MI and stroke, despite receiving PEX.4†
†Retrospective claims analysis of hospitalizations with TTP (N=8203).
Relapse threatens patients
Up to 50% of patients have ≥1 recurrence within 30 days of stopping PEX.1‡
‡Retrospective review of French Reference Centre for TMA registry (N=388).
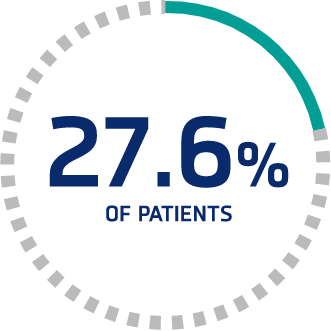
Increased risk of stroke through clinical remission§
Stroke after recovery with PEX occurred in 0% (0/22) of patients with mean normal ADAMTS13 activity (>70%) and in 27.6% (8/29) of patients with ADAMTS13 activity ≤70% (P=0.007).19‖
‖Cohort study of 170 patients with aTTP/iTTP from 1995 to 2018.
Early diagnosis of aTTP/iTTP is critical
CABLIVI is targeted to prevent microthrombi
§Defined as sustained clinical response either with no PEX and no anti-vWF therapy in the last 30 days or with the attainment of ADAMTS13 remission (partial [between 20% and LLN] or complete [≥LLN]), whichever occurs first.20
ADAMTS13=a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin type 1 motif, 13; LLN=lower limit of normal; MI=myocardial infarction; PEX=plasma exchange; TMA=thrombotic microangiopathy; TTP=thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; ULvWF=ultra-large von Willebrand factor; vWF=von Willebrand factor.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. Grall M, Azoulay E, Galicier L, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura misdiagnosed as autoimmune cytopenia: causes of diagnostic errors and consequence on outcome. Experience of the French Thrombotic Microangiopathies Reference Centre. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(4):381-387. doi:10.1002/ajh.24665 2. Kremer Hovinga JA, Vesely SK, Terrell DR, Lämmle B, George JN. Survival and relapse in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2010;115(8):1500-1511. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-09-243790 3. Peyvandi F, Scully M, Kremer Hovinga JA, et al. Caplacizumab reduces the frequency of major thromboembolic events, exacerbations and death in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(7):1448-1452. doi:10.1111/jth.13716 4. Goel R, King KE, Takemoto CM, Ness PM, Tobian AAR. Prognostic risk-stratified score for predicting mortality in hospitalized patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: nationally representative data from 2007 to 2012. Transfusion. 2016;56(6):1451-1458. doi:10.1111/trf.13586 5. Masias C, Wu H, McGookey M, Jay L, Cataland S, Yang S. No major differences in outcomes between the initial and relapse episodes in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: the experience from the Ohio State University Registry. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(3):E73-E75. doi:10.1002/ajh.25002 6. Coppo P, Veyradier A. Current management and therapeutical perspectives in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Presse Med. 2012;41(3 pt 2):e163-e176. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2011.10.024 7. Bommer M, Wölfle-Guter M, Bohl S, Kuchenbauer F. The differential diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic microangiopathies. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018;115(19):327-334. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0327 8. Zheng XL, Vesely SK, Cataland SR, et al. ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(10):2486-2495. doi:10.1111/jth.15006 9. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311 10. National Institutes of Health. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Updated February 2023. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/9430/congenital-thrombotic-thrombocytopenic-purpura 11. Schieppati F, Russo L, Marchetti M, et al. Low levels of ADAMTS-13 with high anti-ADAMTS-13 antibodies during remission of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura highly predict for disease relapse: a multi-institutional study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(8):953-959. doi:10.1002/ajh.25845 12. Knoebl P, Cataland S, Peyvandi F, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label caplacizumab in patients with exacerbations of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in the HERCULES study. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(2):479-484. doi:10.1111/jth.14679 13. Joly BS, Coppo P, Veyradier A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2017;129(21):2836-2846. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-10-709857 14. Sayani FA, Abrams CS. How I treat refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2015;125(25):3860-3867. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-11-551580 15. Scully M, Hunt BJ, Benjamin S, et al; British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies. Br J Haematol. 2012;158(3):323-335. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2012.09167.x 16. Kremer Hovinga JA, Coppo P, Lämmle B, Moake JL, Miyata T, Vanhoorelbeke K. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17020. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.20 17. Holz J-B. The TITAN trial—assessing the efficacy and safety of an anti-von Willebrand factor Nanobody in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfus Apher Sci. 2012;46(3):343-346. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2012.03.027 18. Azoulay E, Bauer PR, Mariotte E, et al; Nine-i Investigators. Expert statement on the ICU management of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45(11):1518-1539. doi:10.1007/s00134-019-05736-5 19. Upreti H, Kasmani J, Dane K, et al. Reduced ADAMTS13 activity during TTP remission is associated with stroke in TTP survivors. Blood. 2019;134(13):1037-1045. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001056 20. Cuker A, Cataland SR, Coppo P, et al; International Working Group for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Redefining outcomes in immune TTP: an international working group consensus report. Blood. 2021;137(14):1855-1861. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009150
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. Grall M, Azoulay E, Galicier L, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura misdiagnosed as autoimmune cytopenia: causes of diagnostic errors and consequence on outcome. Experience of the French Thrombotic Microangiopathies Reference Centre. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(4):381-387. doi:10.1002/ajh.24665 2. Kremer Hovinga JA, Vesely SK, Terrell DR, Lämmle B, George JN. Survival and relapse in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2010;115(8):1500-1511. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-09-243790 3. Peyvandi F, Scully M, Kremer Hovinga JA, et al. Caplacizumab reduces the frequency of major thromboembolic events, exacerbations and death in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(7):1448-1452. doi:10.1111/jth.13716 4. Goel R, King KE, Takemoto CM, Ness PM, Tobian AAR. Prognostic risk-stratified score for predicting mortality in hospitalized patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: nationally representative data from 2007 to 2012. Transfusion. 2016;56(6):1451-1458. doi:10.1111/trf.13586 5. Masias C, Wu H, McGookey M, Jay L, Cataland S, Yang S. No major differences in outcomes between the initial and relapse episodes in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: the experience from the Ohio State University Registry. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(3):E73-E75. doi:10.1002/ajh.25002 6. Coppo P, Veyradier A. Current management and therapeutical perspectives in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Presse Med. 2012;41(3 pt 2):e163-e176. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2011.10.024 7. Bommer M, Wölfle-Guter M, Bohl S, Kuchenbauer F. The differential diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic microangiopathies. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018;115(19):327-334. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0327 8. Zheng XL, Vesely SK, Cataland SR, et al. ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(10):2486-2495. doi:10.1111/jth.15006 9. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311 10. National Institutes of Health. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Updated February 2023. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/9430/congenital-thrombotic-thrombocytopenic-purpura 11. Schieppati F, Russo L, Marchetti M, et al. Low levels of ADAMTS-13 with high anti-ADAMTS-13 antibodies during remission of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura highly predict for disease relapse: a multi-institutional study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(8):953-959. doi:10.1002/ajh.25845 12. Knoebl P, Cataland S, Peyvandi F, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label caplacizumab in patients with exacerbations of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in the HERCULES study. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(2):479-484. doi:10.1111/jth.14679 13. Joly BS, Coppo P, Veyradier A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2017;129(21):2836-2846. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-10-709857 14. Sayani FA, Abrams CS. How I treat refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2015;125(25):3860-3867. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-11-551580 15. Scully M, Hunt BJ, Benjamin S, et al; British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies. Br J Haematol. 2012;158(3):323-335. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2012.09167.x 16. Kremer Hovinga JA, Coppo P, Lämmle B, Moake JL, Miyata T, Vanhoorelbeke K. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17020. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.20 17. Holz J-B. The TITAN trial—assessing the efficacy and safety of an anti-von Willebrand factor Nanobody in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfus Apher Sci. 2012;46(3):343-346. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2012.03.027 18. Azoulay E, Bauer PR, Mariotte E, et al; Nine-i Investigators. Expert statement on the ICU management of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45(11):1518-1539. doi:10.1007/s00134-019-05736-5 19. Upreti H, Kasmani J, Dane K, et al. Reduced ADAMTS13 activity during TTP remission is associated with stroke in TTP survivors. Blood. 2019;134(13):1037-1045. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001056 20. Cuker A, Cataland SR, Coppo P, et al; International Working Group for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Redefining outcomes in immune TTP: an international working group consensus report. Blood. 2021;137(14):1855-1861. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009150
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. Grall M, Azoulay E, Galicier L, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura misdiagnosed as autoimmune cytopenia: causes of diagnostic errors and consequence on outcome. Experience of the French Thrombotic Microangiopathies Reference Centre. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(4):381-387. doi:10.1002/ajh.24665 2. Kremer Hovinga JA, Vesely SK, Terrell DR, Lämmle B, George JN. Survival and relapse in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2010;115(8):1500-1511. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-09-243790 3. Peyvandi F, Scully M, Kremer Hovinga JA, et al. Caplacizumab reduces the frequency of major thromboembolic events, exacerbations and death in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(7):1448-1452. doi:10.1111/jth.13716 4. Goel R, King KE, Takemoto CM, Ness PM, Tobian AAR. Prognostic risk-stratified score for predicting mortality in hospitalized patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: nationally representative data from 2007 to 2012. Transfusion. 2016;56(6):1451-1458. doi:10.1111/trf.13586 5. Masias C, Wu H, McGookey M, Jay L, Cataland S, Yang S. No major differences in outcomes between the initial and relapse episodes in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: the experience from the Ohio State University Registry. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(3):E73-E75. doi:10.1002/ajh.25002 6. Coppo P, Veyradier A. Current management and therapeutical perspectives in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Presse Med. 2012;41(3 pt 2):e163-e176. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2011.10.024 7. Bommer M, Wölfle-Guter M, Bohl S, Kuchenbauer F. The differential diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic microangiopathies. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018;115(19):327-334. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0327 8. Zheng XL, Vesely SK, Cataland SR, et al. ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(10):2486-2495. doi:10.1111/jth.15006 9. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311 10. National Institutes of Health. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Updated February 2023. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/9430/congenital-thrombotic-thrombocytopenic-purpura 11. Schieppati F, Russo L, Marchetti M, et al. Low levels of ADAMTS-13 with high anti-ADAMTS-13 antibodies during remission of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura highly predict for disease relapse: a multi-institutional study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(8):953-959. doi:10.1002/ajh.25845 12. Knoebl P, Cataland S, Peyvandi F, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label caplacizumab in patients with exacerbations of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in the HERCULES study. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(2):479-484. doi:10.1111/jth.14679 13. Joly BS, Coppo P, Veyradier A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2017;129(21):2836-2846. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-10-709857 14. Sayani FA, Abrams CS. How I treat refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2015;125(25):3860-3867. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-11-551580 15. Scully M, Hunt BJ, Benjamin S, et al; British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies. Br J Haematol. 2012;158(3):323-335. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2012.09167.x 16. Kremer Hovinga JA, Coppo P, Lämmle B, Moake JL, Miyata T, Vanhoorelbeke K. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17020. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.20 17. Holz J-B. The TITAN trial—assessing the efficacy and safety of an anti-von Willebrand factor Nanobody in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfus Apher Sci. 2012;46(3):343-346. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2012.03.027 18. Azoulay E, Bauer PR, Mariotte E, et al; Nine-i Investigators. Expert statement on the ICU management of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45(11):1518-1539. doi:10.1007/s00134-019-05736-5 19. Upreti H, Kasmani J, Dane K, et al. Reduced ADAMTS13 activity during TTP remission is associated with stroke in TTP survivors. Blood. 2019;134(13):1037-1045. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001056 20. Cuker A, Cataland SR, Coppo P, et al; International Working Group for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Redefining outcomes in immune TTP: an international working group consensus report. Blood. 2021;137(14):1855-1861. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009150
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. Grall M, Azoulay E, Galicier L, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura misdiagnosed as autoimmune cytopenia: causes of diagnostic errors and consequence on outcome. Experience of the French Thrombotic Microangiopathies Reference Centre. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(4):381-387. doi:10.1002/ajh.24665 2. Kremer Hovinga JA, Vesely SK, Terrell DR, Lämmle B, George JN. Survival and relapse in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2010;115(8):1500-1511. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-09-243790 3. Peyvandi F, Scully M, Kremer Hovinga JA, et al. Caplacizumab reduces the frequency of major thromboembolic events, exacerbations and death in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(7):1448-1452. doi:10.1111/jth.13716 4. Goel R, King KE, Takemoto CM, Ness PM, Tobian AAR. Prognostic risk-stratified score for predicting mortality in hospitalized patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: nationally representative data from 2007 to 2012. Transfusion. 2016;56(6):1451-1458. doi:10.1111/trf.13586 5. Masias C, Wu H, McGookey M, Jay L, Cataland S, Yang S. No major differences in outcomes between the initial and relapse episodes in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: the experience from the Ohio State University Registry. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(3):E73-E75. doi:10.1002/ajh.25002 6. Coppo P, Veyradier A. Current management and therapeutical perspectives in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Presse Med. 2012;41(3 pt 2):e163-e176. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2011.10.024 7. Bommer M, Wölfle-Guter M, Bohl S, Kuchenbauer F. The differential diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic microangiopathies. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018;115(19):327-334. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0327 8. Zheng XL, Vesely SK, Cataland SR, et al. ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(10):2486-2495. doi:10.1111/jth.15006 9. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311 10. National Institutes of Health. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Updated February 2023. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/9430/congenital-thrombotic-thrombocytopenic-purpura 11. Schieppati F, Russo L, Marchetti M, et al. Low levels of ADAMTS-13 with high anti-ADAMTS-13 antibodies during remission of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura highly predict for disease relapse: a multi-institutional study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(8):953-959. doi:10.1002/ajh.25845 12. Knoebl P, Cataland S, Peyvandi F, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label caplacizumab in patients with exacerbations of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in the HERCULES study. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(2):479-484. doi:10.1111/jth.14679 13. Joly BS, Coppo P, Veyradier A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2017;129(21):2836-2846. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-10-709857 14. Sayani FA, Abrams CS. How I treat refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2015;125(25):3860-3867. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-11-551580 15. Scully M, Hunt BJ, Benjamin S, et al; British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies. Br J Haematol. 2012;158(3):323-335. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2012.09167.x 16. Kremer Hovinga JA, Coppo P, Lämmle B, Moake JL, Miyata T, Vanhoorelbeke K. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17020. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.20 17. Holz J-B. The TITAN trial—assessing the efficacy and safety of an anti-von Willebrand factor Nanobody in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfus Apher Sci. 2012;46(3):343-346. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2012.03.027 18. Azoulay E, Bauer PR, Mariotte E, et al; Nine-i Investigators. Expert statement on the ICU management of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45(11):1518-1539. doi:10.1007/s00134-019-05736-5 19. Upreti H, Kasmani J, Dane K, et al. Reduced ADAMTS13 activity during TTP remission is associated with stroke in TTP survivors. Blood. 2019;134(13):1037-1045. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001056 20. Cuker A, Cataland SR, Coppo P, et al; International Working Group for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Redefining outcomes in immune TTP: an international working group consensus report. Blood. 2021;137(14):1855-1861. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009150
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. Grall M, Azoulay E, Galicier L, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura misdiagnosed as autoimmune cytopenia: causes of diagnostic errors and consequence on outcome. Experience of the French Thrombotic Microangiopathies Reference Centre. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(4):381-387. doi:10.1002/ajh.24665 2. Kremer Hovinga JA, Vesely SK, Terrell DR, Lämmle B, George JN. Survival and relapse in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2010;115(8):1500-1511. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-09-243790 3. Peyvandi F, Scully M, Kremer Hovinga JA, et al. Caplacizumab reduces the frequency of major thromboembolic events, exacerbations and death in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(7):1448-1452. doi:10.1111/jth.13716 4. Goel R, King KE, Takemoto CM, Ness PM, Tobian AAR. Prognostic risk-stratified score for predicting mortality in hospitalized patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: nationally representative data from 2007 to 2012. Transfusion. 2016;56(6):1451-1458. doi:10.1111/trf.13586 5. Masias C, Wu H, McGookey M, Jay L, Cataland S, Yang S. No major differences in outcomes between the initial and relapse episodes in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: the experience from the Ohio State University Registry. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(3):E73-E75. doi:10.1002/ajh.25002 6. Coppo P, Veyradier A. Current management and therapeutical perspectives in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Presse Med. 2012;41(3 pt 2):e163-e176. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2011.10.024 7. Bommer M, Wölfle-Guter M, Bohl S, Kuchenbauer F. The differential diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic microangiopathies. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018;115(19):327-334. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0327 8. Zheng XL, Vesely SK, Cataland SR, et al. ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(10):2486-2495. doi:10.1111/jth.15006 9. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311 10. National Institutes of Health. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Updated February 2023. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/9430/congenital-thrombotic-thrombocytopenic-purpura 11. Schieppati F, Russo L, Marchetti M, et al. Low levels of ADAMTS-13 with high anti-ADAMTS-13 antibodies during remission of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura highly predict for disease relapse: a multi-institutional study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(8):953-959. doi:10.1002/ajh.25845 12. Knoebl P, Cataland S, Peyvandi F, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label caplacizumab in patients with exacerbations of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in the HERCULES study. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(2):479-484. doi:10.1111/jth.14679 13. Joly BS, Coppo P, Veyradier A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2017;129(21):2836-2846. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-10-709857 14. Sayani FA, Abrams CS. How I treat refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2015;125(25):3860-3867. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-11-551580 15. Scully M, Hunt BJ, Benjamin S, et al; British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies. Br J Haematol. 2012;158(3):323-335. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2012.09167.x 16. Kremer Hovinga JA, Coppo P, Lämmle B, Moake JL, Miyata T, Vanhoorelbeke K. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17020. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.20 17. Holz J-B. The TITAN trial—assessing the efficacy and safety of an anti-von Willebrand factor Nanobody in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfus Apher Sci. 2012;46(3):343-346. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2012.03.027 18. Azoulay E, Bauer PR, Mariotte E, et al; Nine-i Investigators. Expert statement on the ICU management of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45(11):1518-1539. doi:10.1007/s00134-019-05736-5 19. Upreti H, Kasmani J, Dane K, et al. Reduced ADAMTS13 activity during TTP remission is associated with stroke in TTP survivors. Blood. 2019;134(13):1037-1045. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001056 20. Cuker A, Cataland SR, Coppo P, et al; International Working Group for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Redefining outcomes in immune TTP: an international working group consensus report. Blood. 2021;137(14):1855-1861. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009150
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
CABLIVI is contraindicated in patients with a previous severe hypersensitivity reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of its excipients. Hypersensitivity reactions have included urticaria.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Hemorrhage:
- CABLIVI increases the risk of bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of epistaxis, gingival bleeding, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and metrorrhagia were each reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, bleeding events occurred in approximately 58% of patients on CABLIVI versus 43% of patients on placebo.
- In the postmarketing setting cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI.
- The risk of bleeding is increased in patients with underlying coagulopathies (e.g. hemophilia, other coagulation factor deficiencies). It is also increased with concomitant use of CABLIVI with drugs affecting hemostasis and coagulation.
- Avoid concomitant use of CABLIVI with antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. If clinically significant bleeding occurs, interrupt use of CABLIVI. Von Willebrand factor concentrate may be administered to rapidly correct hemostasis. If CABLIVI is restarted, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
- Withhold CABLIVI for 7 days prior to elective surgery, dental procedures or other invasive interventions. If emergency surgery is needed, the use of von Willebrand factor concentrate may be considered to correct hemostasis. After the risk of surgical bleeding has resolved, and CABLIVI is resumed, monitor closely for signs of bleeding.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
The most common adverse reactions (>15% of patients) were epistaxis (29%), headache (21%) and gingival bleeding (16%).
CONCOMITANT USE OF ANTICOAGULANTS OR ANTIPLATELET AGENTS:
Concomitant use of CABLIVI with any anticoagulant or antiplatelet agent may increase the risk of bleeding. Avoid concomitant use when possible. Assess and monitor closely for bleeding with concomitant use.
PREGNANCY:
There are no available data on CABLIVI use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
-
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions: CABLIVI may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding.
-
Maternal adverse reactions: All patients receiving CABLIVI, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. Pregnant women receiving CABLIVI should be carefully monitored for evidence of excessive bleeding.
INDICATIONS:
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
References: 1. Grall M, Azoulay E, Galicier L, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura misdiagnosed as autoimmune cytopenia: causes of diagnostic errors and consequence on outcome. Experience of the French Thrombotic Microangiopathies Reference Centre. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(4):381-387. doi:10.1002/ajh.24665 2. Kremer Hovinga JA, Vesely SK, Terrell DR, Lämmle B, George JN. Survival and relapse in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2010;115(8):1500-1511. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-09-243790 3. Peyvandi F, Scully M, Kremer Hovinga JA, et al. Caplacizumab reduces the frequency of major thromboembolic events, exacerbations and death in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(7):1448-1452. doi:10.1111/jth.13716 4. Goel R, King KE, Takemoto CM, Ness PM, Tobian AAR. Prognostic risk-stratified score for predicting mortality in hospitalized patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: nationally representative data from 2007 to 2012. Transfusion. 2016;56(6):1451-1458. doi:10.1111/trf.13586 5. Masias C, Wu H, McGookey M, Jay L, Cataland S, Yang S. No major differences in outcomes between the initial and relapse episodes in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: the experience from the Ohio State University Registry. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(3):E73-E75. doi:10.1002/ajh.25002 6. Coppo P, Veyradier A. Current management and therapeutical perspectives in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Presse Med. 2012;41(3 pt 2):e163-e176. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2011.10.024 7. Bommer M, Wölfle-Guter M, Bohl S, Kuchenbauer F. The differential diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic microangiopathies. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018;115(19):327-334. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0327 8. Zheng XL, Vesely SK, Cataland SR, et al. ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(10):2486-2495. doi:10.1111/jth.15006 9. Scully M, Cataland SR, Peyvandi F, et al; HERCULES Investigators. Caplacizumab treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):335-346. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1806311 10. National Institutes of Health. Congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Updated February 2023. Accessed April 14, 2023. https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/9430/congenital-thrombotic-thrombocytopenic-purpura 11. Schieppati F, Russo L, Marchetti M, et al. Low levels of ADAMTS-13 with high anti-ADAMTS-13 antibodies during remission of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura highly predict for disease relapse: a multi-institutional study. Am J Hematol. 2020;95(8):953-959. doi:10.1002/ajh.25845 12. Knoebl P, Cataland S, Peyvandi F, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label caplacizumab in patients with exacerbations of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in the HERCULES study. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(2):479-484. doi:10.1111/jth.14679 13. Joly BS, Coppo P, Veyradier A. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2017;129(21):2836-2846. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-10-709857 14. Sayani FA, Abrams CS. How I treat refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2015;125(25):3860-3867. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-11-551580 15. Scully M, Hunt BJ, Benjamin S, et al; British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombotic microangiopathies. Br J Haematol. 2012;158(3):323-335. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2012.09167.x 16. Kremer Hovinga JA, Coppo P, Lämmle B, Moake JL, Miyata T, Vanhoorelbeke K. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17020. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.20 17. Holz J-B. The TITAN trial—assessing the efficacy and safety of an anti-von Willebrand factor Nanobody in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfus Apher Sci. 2012;46(3):343-346. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2012.03.027 18. Azoulay E, Bauer PR, Mariotte E, et al; Nine-i Investigators. Expert statement on the ICU management of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Intensive Care Med. 2019;45(11):1518-1539. doi:10.1007/s00134-019-05736-5 19. Upreti H, Kasmani J, Dane K, et al. Reduced ADAMTS13 activity during TTP remission is associated with stroke in TTP survivors. Blood. 2019;134(13):1037-1045. doi:10.1182/blood.2019001056 20. Cuker A, Cataland SR, Coppo P, et al; International Working Group for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Redefining outcomes in immune TTP: an international working group consensus report. Blood. 2021;137(14):1855-1861. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009150
